Industrial-grade switches and enterprise-class switches both play an important role in network infrastructure, but they have significant differences in design and functionality. The following is a deep analysis of the differences between these two types of switches:
Design concept: mainly to meet the internal network communication needs of enterprises, build a high-speed and reliable network backbone, and support large-scale data transmission and control.
Purpose: It is widely used in data centers, large enterprise networks, cloud computing platforms, and other scenarios, and is suitable for daily office work, data exchange, video conferencing, and other needs of enterprises.
Industrial-grade switch:
Design concept: designed for industrial automation, intelligent manufacturing, energy monitoring and other industrial fields, focusing on durability, protection and stability.
Purpose: Provide reliable network support for critical tasks in industrial automation, intelligent manufacturing, smart cities, energy and power, and other fields. These fields often face extreme working environments, such as high temperature, high humidity, strong electromagnetic interference, etc.

Figure 1: Application Scenario of Industrial-Grade Switch
Structural design: Modular design is usually used, which has high flexibility and scalability.
Durability: Although it also has high reliability, its performance in harsh environments may not be as good as industrial-grade switches.
Industrial-grade switch:
Structural design: Utilizing a sturdy and durable casing and high-quality components, it boasts waterproof, dustproof, and shock-resistant features.
Durability: Industrial-grade electronic components are used, with higher protection levels and longer service life. It can normally work between -40℃ and 75℃, and adopts dual power supply mode to ensure continuous operation in case of power failure.

Figure 2: The hardware protection of industrial-grade switches can work normally in harsh environments such as severe cold and heat
Data transmission performance: usually has high data transmission rate and throughput.
Redundant function: Although it also has redundant function, it usually requires running the STP protocol, with a redundant time of more than 10 seconds, which is not suitable for industrial environments that require rapid response.
Industrial-grade switch:
Data transmission performance: Supporting multiple network topologies, it can monitor network status in real time and flexibly configure according to actual needs.
Redundant function: It has the functions of rapid networking and multilateral redundancy, with a redundancy time usually less than 20 milliseconds, which can quickly respond to network changes and ensure the continuity and stability of data transmission.
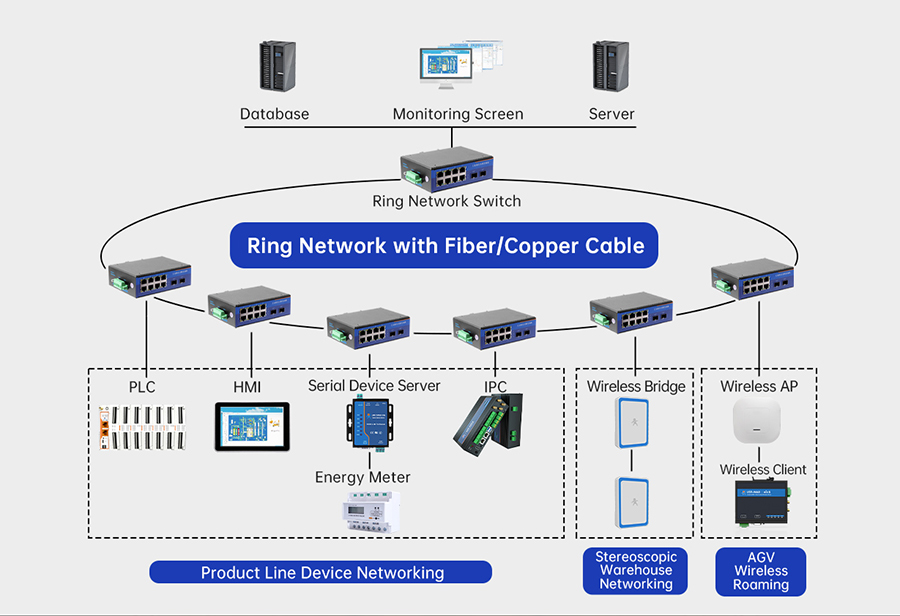
Figure 3: The ring network redundancy of industrial-grade switches achieves the effect of uninterrupted communication
Anti-interference performance: Although it is also strong, it is usually not comparable to industrial-grade switches.
Industrial-grade switch:
Anti-interference performance: It performs well in industrial sites with complex electromagnetic environments. Data ports usually have lightning protection functions and can work normally under extreme weather conditions such as lightning. At the same time, through the use of special circuit design and filtering technology, it can effectively suppress the interference of fast pulse trains and ensure the stability and reliability of data transmission.
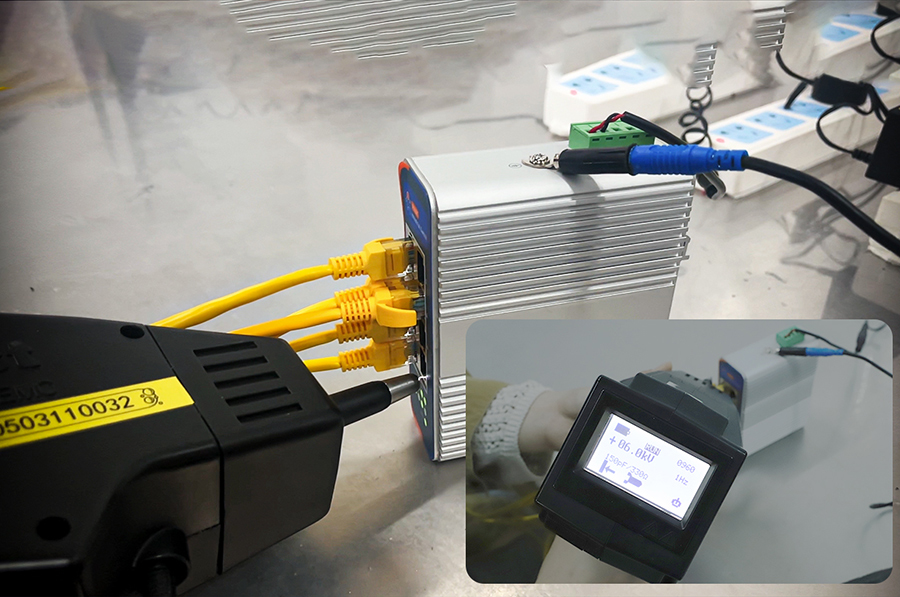

Figure 4: Lightning protection test of industrial-grade switches, which can achieve normal operation under 6000V lightning or surge voltage
Advanced network functions: Support various advanced network management functions, such as VLAN division, QoS policies, access control, etc., to ensure efficient operation and security protection of the network.
Compatibility: It usually has good compatibility with other network devices within the enterprise.
Industrial-grade switch:
Advanced network functions: more emphasis on interface docking with industrial automation equipment, usually supporting multiple network protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, etc., for communication and data exchange between devices.
Compatibility: widely compatible with various industrial automation equipment and systems.
Cost: relatively low, more suitable for general enterprise network communication environments.
Maintenance: Typically, it is relatively straightforward, as enterprise-level network environments are relatively stable and easy to manage.
Industrial-grade switch:
Cost: Due to the need for higher standards and requirements in design and manufacturing, the cost is usually higher.
Maintenance: When used in critical production environments, maintenance and replacement costs may also be higher. However, the long lifespan and high reliability of industrial-grade switches help reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Industrial-grade switches and enterprise-class switches exhibit notable differences in design philosophy, structural design and durability, data transmission performance and redundancy, anti-interference performance, advanced network functions and compatibility, as well as cost and maintenance. When selecting a switch, one should weigh and make decisions based on the actual application scenarios and requirements.