With the Internet of Things (IoT) technology being highly concerned in recent years, many well-known technologies and related promotion alliances, such as NB-IoT, LTE-M (Long Term Evolution, Category M1), Wi-SUN and Sigfox, are competing in the market. LoRa technology also has a lot of deployment and attention in the world.
LPWAN (Low-Power Wide-Area Network) is designed for Internet of Things applications with low bandwidth, low power consumption, long distance and large number of connections. LoRa has a more mature ecological chain and faster commercial pace, and is expected to maintain a doubling growth rate in the next few years.
The wireless technology in the application of the Internet of Things is mainly divided into two kinds, one is the short-range wireless technology, such as Bluetooth/WiFi/ZigBee. The other is the technology that makes up the wide area network, such as 2G/3G/4G. The advantages and disadvantages of each technology are very obvious. Before the LPWAN technology was produced, usually only one of long-distance and low power consumption could be chosen. With the advent of LPWAN technology, the problems of fish and bear's paw are balanced, and in addition to achieving longer distance communication and ultra-low power consumption, additional repeater costs can be saved.
LoRa is a typical LPWAN communication technology, which is an ultra-long-distance wireless transmission scheme based on spread spectrum technology adopted and promoted by Semtech Company in the United States. This transmission scheme changes the trade-off between transmission distance and power consumption in the past, and provides a simple system that can achieve long-distance, long battery life and large capacity. Thereby expanding the sensing network. At present, LoRa mainly operates in the global free frequency band, including 433, 868, 915MHz and so on.
1. The receiving sensitivity is improved and the power consumption is reduced.
A link budget of up to 157 db enables communication distances of up to 15 km (depending on the environment). The receive current is only 10 mA and the sleep current is 200 nA, which significantly delays battery life.
2. The gateway/concentrator based on this technology supports parallel processing of multiple channels and multiple data rates, and the system capacity is large.
The gateway is the bridge between the nodes and the IP network (via 2G/3G/4G or Ethernet), and each gateway can handle 5 million communications between the nodes per day (assuming 10 Bytes are sent each time, and the network occupancy is 10%). If the gateway is installed at the location of the existing mobile communication base station with a transmission power of 20dBm (100mW), it can cover about 2 kilometers in the urban environment with dense buildings, and 10 kilometers in the suburbs with lower density.
3. Systems based on terminals and concentrators/gateways can support ranging and positioning.
LoRa's measurement of distance is based on the air transmission time of signals instead of the traditional RSSI (Received Signal Sterngth Ind), while positioning is based on the measurement of the air transmission time difference between multiple points (gateways) and one point (node). Its positioning accuracy is up to 5 m (assuming a range of 10 km).
LoRa network is mainly composed of terminal (built-in LoRa module), gateway (or base station), network server and application server. Its network architecture is a typical star topology. In this network architecture, the LoRa gateway is a transparent transmission relay, connecting the terminal equipment and the back-end central server. An end device communicates with one or more gateways using a single hop. All nodes communicate with the gateway in both directions.
LoRa's end nodes may be a variety of devices, such as water and gas meters, smoke alarms, pet trackers, etc. These nodes are firstly connected with the LoRa gateway through the LoRa wireless communication, and then connected to the network server through the 3G network or the Ethernet network. The gateway communicates with the network server through the TCP/IP protocol.
LoRa terminal equipment
LoRa's end nodes may be a variety of devices, such as water and gas meters, smoke alarms, pet trackers, etc. These nodes are firstly connected with the LoRa gateway through the LoRa wireless communication, and then connected to the network server through the 3G network or the Ethernet network. The gateway communicates with the network server through the TCP/IP protocol.
The LoRa network divides the terminal equipment into three types: A/B/C:
Class A: Two-way communication terminal equipment. This class of terminal equipment allows two-way communication, with each terminal equipment uplink transmission being accompanied by two downlink receive windows. The transmission time slot of the terminal equipment is based on its own communication requirements, and its fine-tuning is based on the ALOHA protocol.
Class A equipment has the lowest power consumption, and the downlink communication of the base station can only be conducted after the uplink communication of the terminal
Class B: bidirectional communication terminal equipment with preset receiving time slots. This kind of terminal equipment will open the extra receiving window in the preset time. In order to achieve this purpose, the terminal equipment will synchronously receive a Beacon from the gateway, and synchronize the time of the base station and the module through the Beacon.
Class B terminals may make the base station aware that the terminal is receiving data
Class C: Two-way communication terminal equipment with maximum receiving window. This type of terminal device has a continuously open receive window that is closed only during transmission.
Class C devices have the longest receive window and consume the most power
IV. Application Scenario of LoRa
LoRaWAN-based network can provide secure two-way communication with long data transmission distance, and cover urban areas with the least network infrastructure. LoRa will be widely used in smart agriculture, smart buildings, smart logistics and other application scenarios.
For agriculture, low power and low cost sensors are urgently needed. The application of temperature and humidity, carbon dioxide, salinity and other sensors is of great significance for agriculture to increase production and reduce the consumption of water resources, and these data indicators will not change significantly in a short time, the amount of data is small and the requirement for real-time is not high, so LoRa is undoubtedly the best choice.
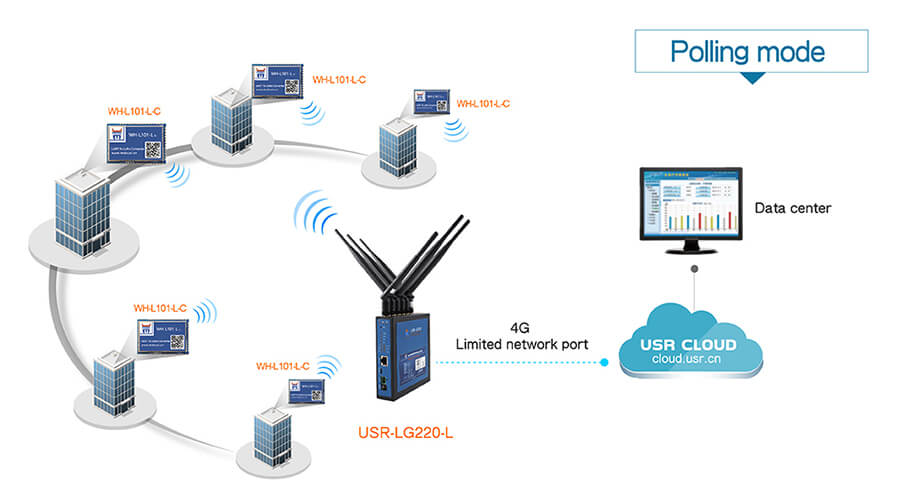
For the transformation of the building, sensors such as temperature and humidity, safety, harmful gas and water flow monitoring are added and the monitored information is uploaded regularly, which facilitates the supervision of managers and users. Generally speaking, the communication of these sensors does not need to be particularly frequent or ensure a particularly good quality of service, and the portable home gateway can meet the needs, so LoRa is a more appropriate choice in this scenario.
In the automatic industrial production environment, a large number of intelligent technologies are applied, and all kinds of information and data are converged in the network, so the characteristics of the selected network are directly related to the execution quality of the production plan. LoRa is a logical choice for scenarios that require low-cost sensors with low-power and long-life batteries to track and monitor the status of devices.
The logistics industry covers a very wide range of geographical areas, so when choosing a network, the first consideration is low investment and high working life. In order to be able to track the pallets and determine the location and status of the cargo, the freight company needs that the facilities involved in the entire logistics process are covered by the network, so the network nodes are not only economical enough to be laid on a large scale, but also mobile enough to be installed on the transport vehicle as a mobile gateway.In this way, NB-IoT technology, which needs to rely on 4G base station network, obviously can not meet this requirement, while LoRa's low cost, high battery life, high mobility, and the stability of communication when moving at high speed make it unique in the field of intelligent logistics.
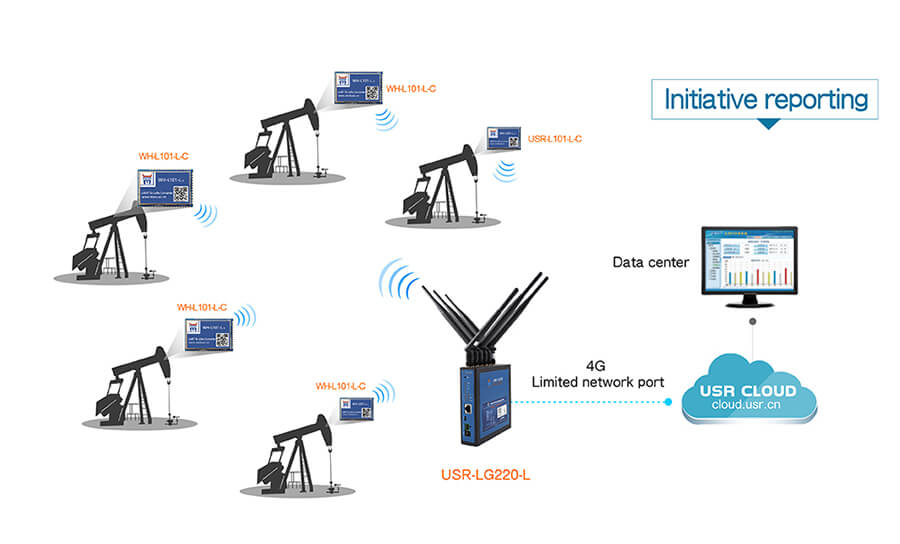
In the new wave of development of the Internet of Things, in the field of low-power wide area network, under the background of large-scale deployment and application in developed markets, domestic participants also promote the large-scale deployment and application of LoRa network in China with open wisdom. The domestic operator-level LoRa network formed by the concept of shared economy will also become the core area of the global LoRa layout.
At present, NB-IoT and LoRa, the two mainstream Internet of Things networks in the world, are developing rapidly in China. According to the statistics of relevant departments, more than 1,000 Internet of Things application products have landed in various provinces of China.It is reported that 70% of enterprises actively seek mature, reliable and fast landing Internet of Things products, most of them purchase NB-IoT and LoRa Internet of Things solutions from Fuzhou Xiecheng Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd., including LoRa gateway, smoke sensing, water monitoring, infrared detection, positioning, row insertion and other dozens of Internet of Things products. In addition, NB-IoT and LoRa Internet of Things products will be developed in order to quickly develop Internet of Things business.It has become the leader of the Internet of Things in all parts of the country.The situation of "looking at China from the development of the Internet of Things in the world" is gradually taking shape.
Summary: Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) is an indispensable part of the Internet of Things. It is flexible and scalable, and its scale can be large or small. This is what the Internet of Things industry needs in the growth and exploration stage, and it can be said to be the most suitable technology for the Internet of things. LoRa is secure and reliable, with features such as two-way authentication, end-to-end encryption and integrity protection. It is comprehensive and forward-looking in security design, but the security of the Internet of Things can not be ignored and needs the joint efforts of the industry to continue to promote.

